How do I upgrade my MySQL 5.7 database to MySQL 8?
Basically, upgrading the MySQL version is a relatively simple process – the old data must be exported into an SQL file and imported into the new database. This article guides you through this and applies to both hosting in the Control Panel and in Cloudpit.
Schematic upgrade process
- Find the configuration file of your application. This is located directly on the web space; the exact location varies depending on the application.
- Save the values for the database name, database user, and database password in a file. You will need these values for the MySQL upgrade.
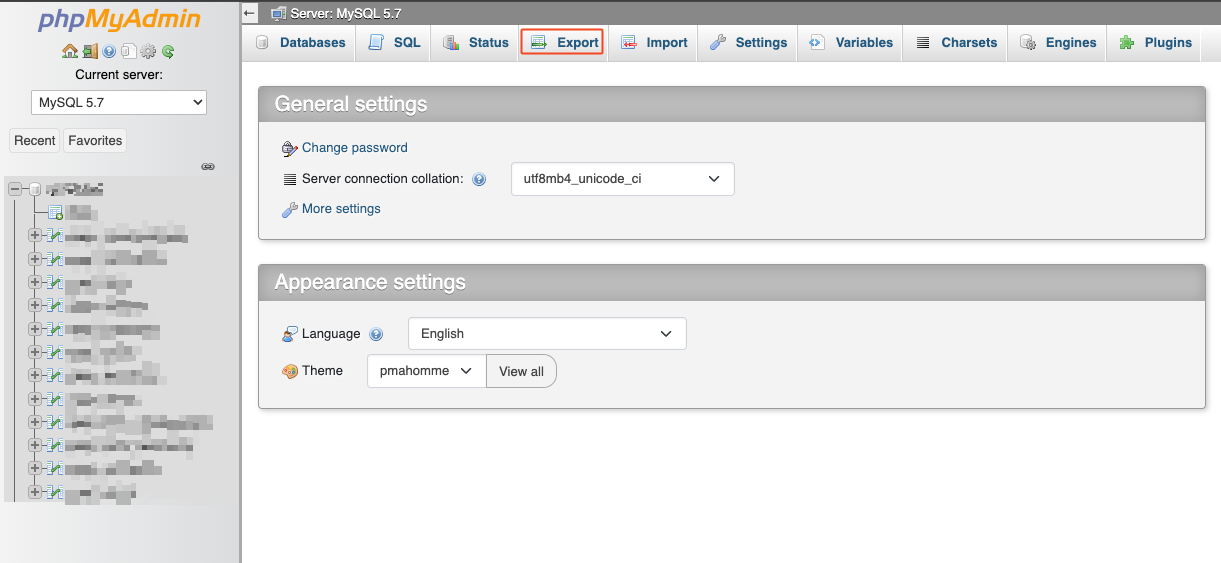
- Log in with these values to phpMyAdmin and export the database as an SQL file.
- Create a new MySQL 8 database and log in to it.
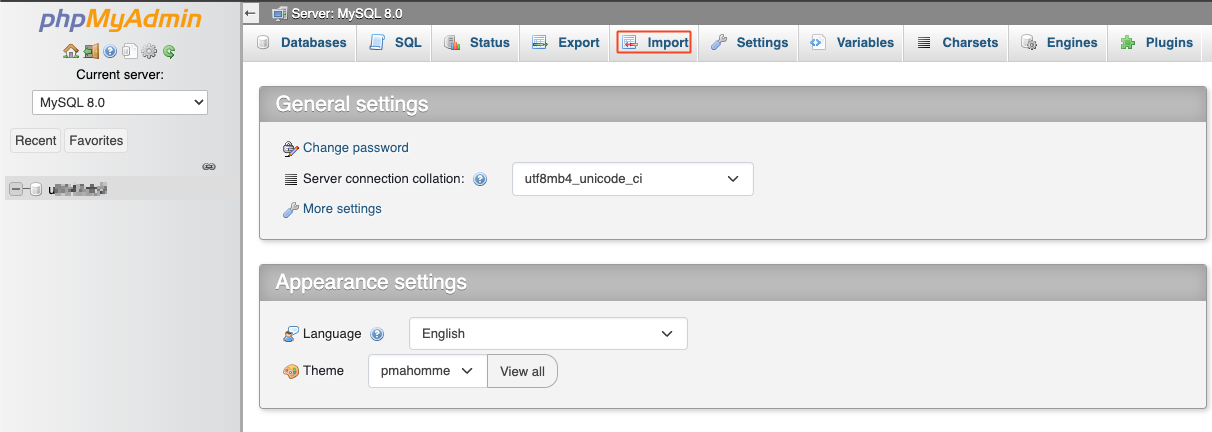
- Import the SQL file exported in step 3 into the new database.
- Adjust the values for the database name, database user, and database password accordingly in the configuration file of your application so that they correspond to those for the MySQL 8 database.
Once you have completed all steps successfully, your database has been successfully upgraded to MySQL 8 and your application now uses it.
Detailed instructions for WordPress in CloudPit
1. Open your WordPress installation via Webhosting [manage] → on the left tab [DOMAINS] – for the affected domain, you will now see the path to your WordPress installation.
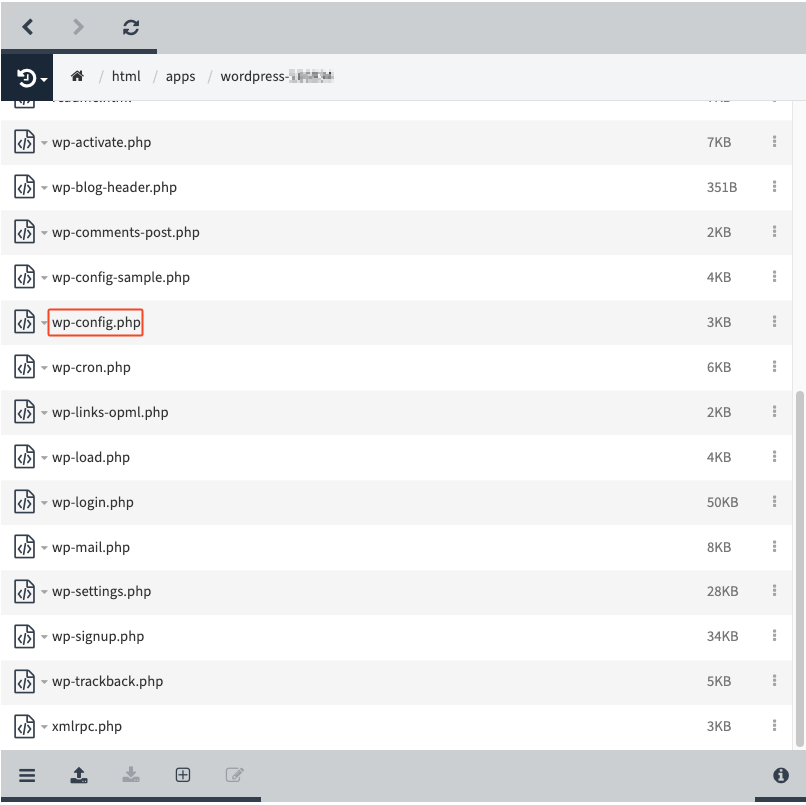
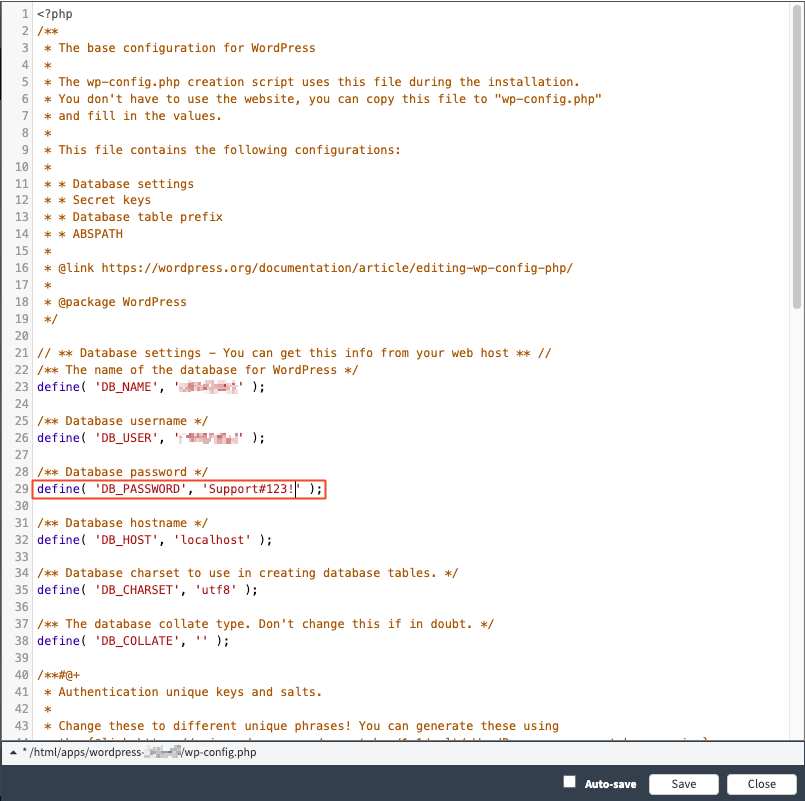
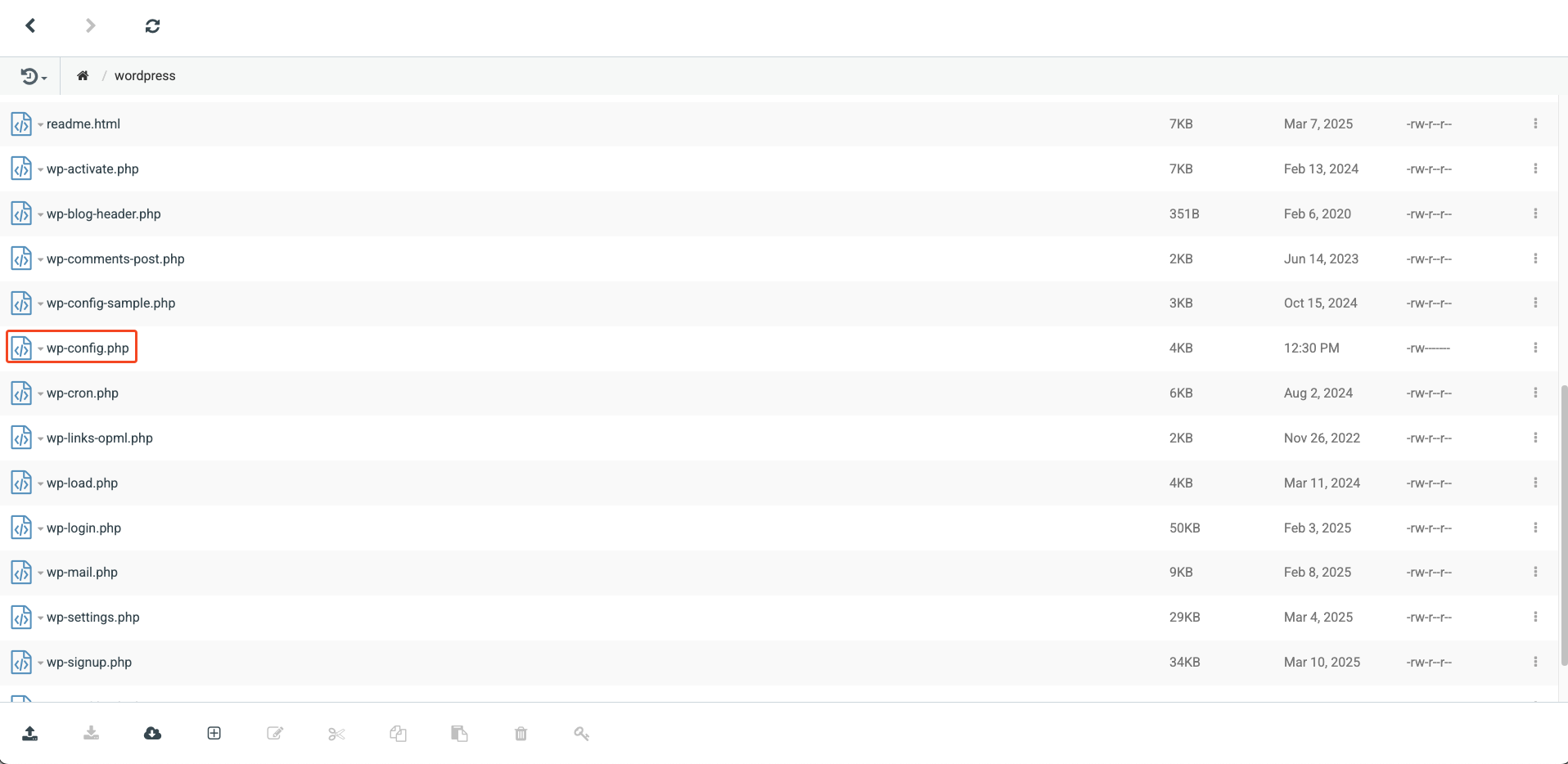
2. In the specified folder, you will find a file called "wp-config.php" which contains the database information including the password. To access it, go to [FTP] → [WEB-FTP], right-click on the file "wp-config.php".
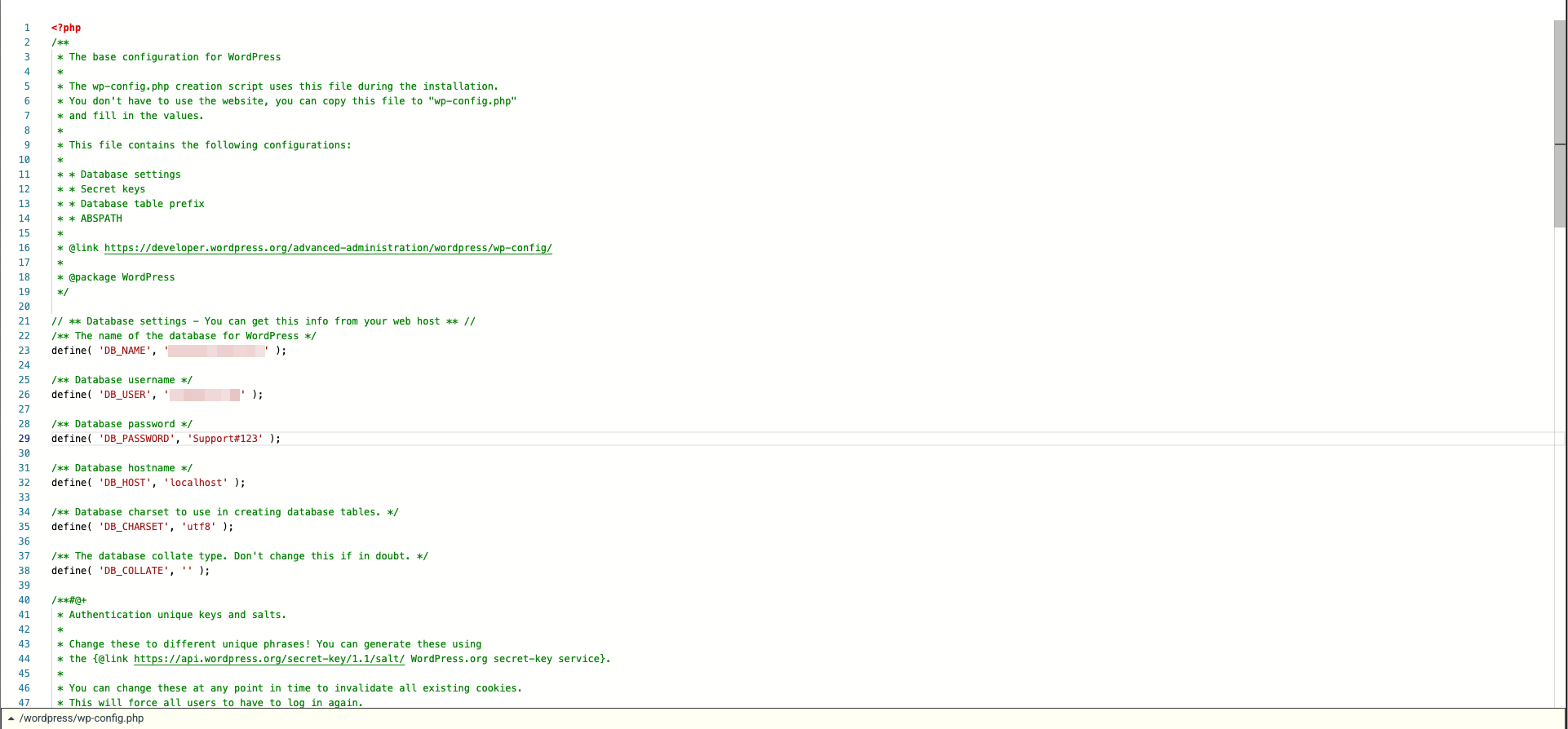
3. Use the data found in step 2 to log in to the corresponding database via [DATABASES] → for the affected database under [ACTIONS] → [Open PhpMyAdmin] . Then export the database.
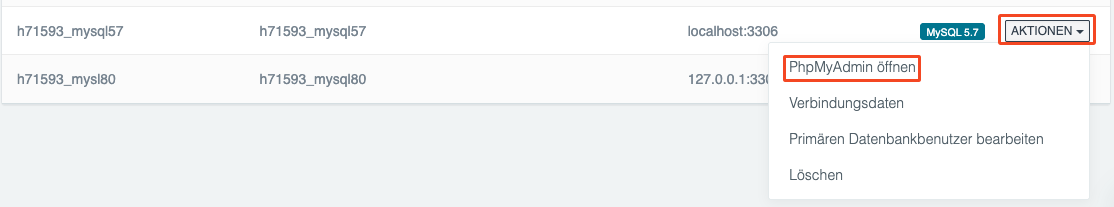
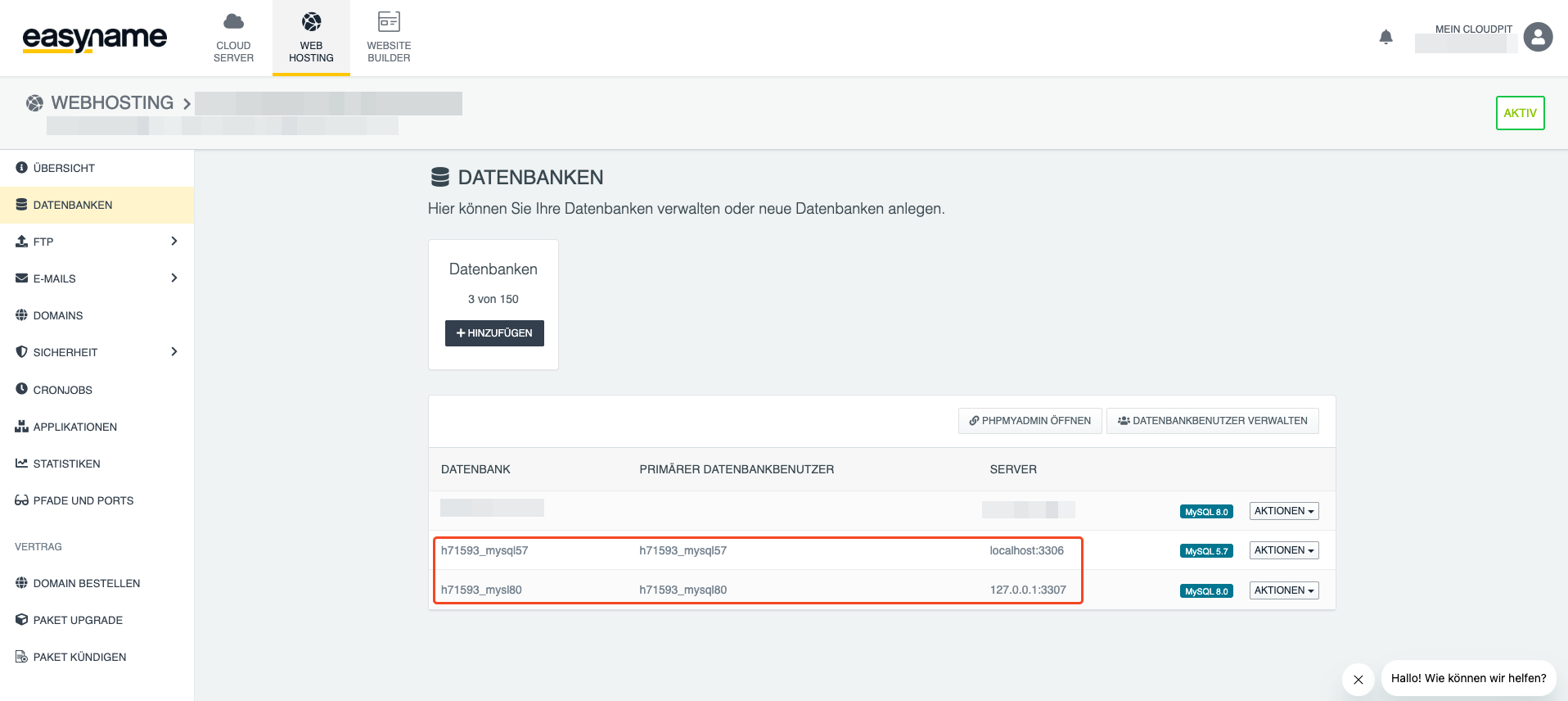
4. Create a new database with MySQL 8 and the same password. Also log in via [Open PhpMyAdmin].
Before you can import the database, you need to edit it. Open the exported database file in a text editor of your choice. Look for the following lines, which are usually between lines 21 and 24:
-- Database: `XXXX`
--
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `XXXX` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
USE `XXXX`;
Replace "XXXX" with the name of the new database and save the changes.
5. Import the previously exported database into the newly created MySQL 8 database.
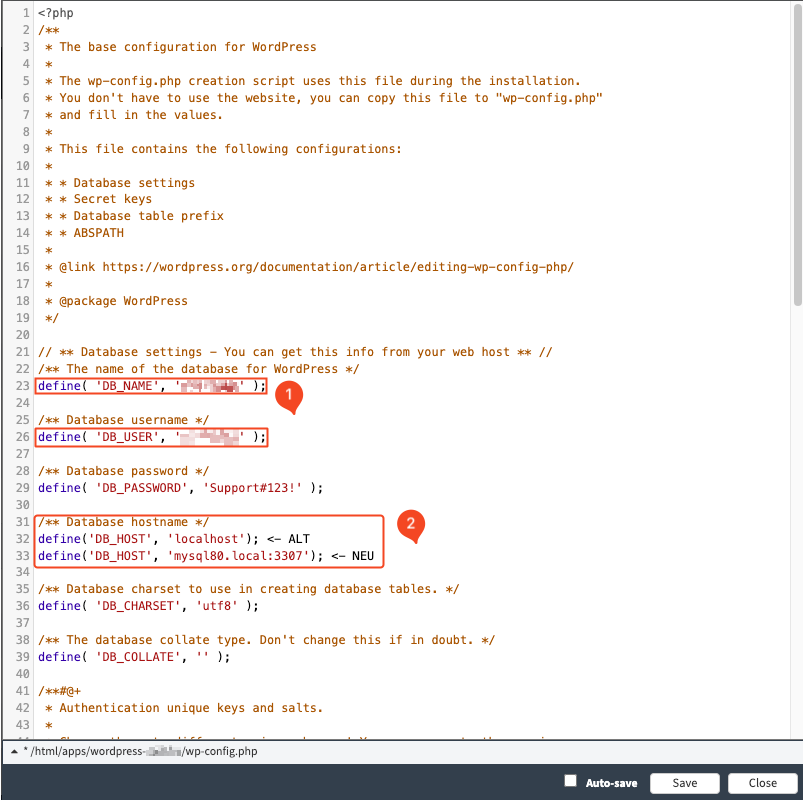
6. Now you need to adjust the host and database name. In the case of WordPress, you can do this in the "wp-config.php" file. Depending on whether you manage your web hosting in our Control Panel or in Cloudpit, the database server differs.
For customers in CloudPit, the correct address is 127.0.0.1:3307.
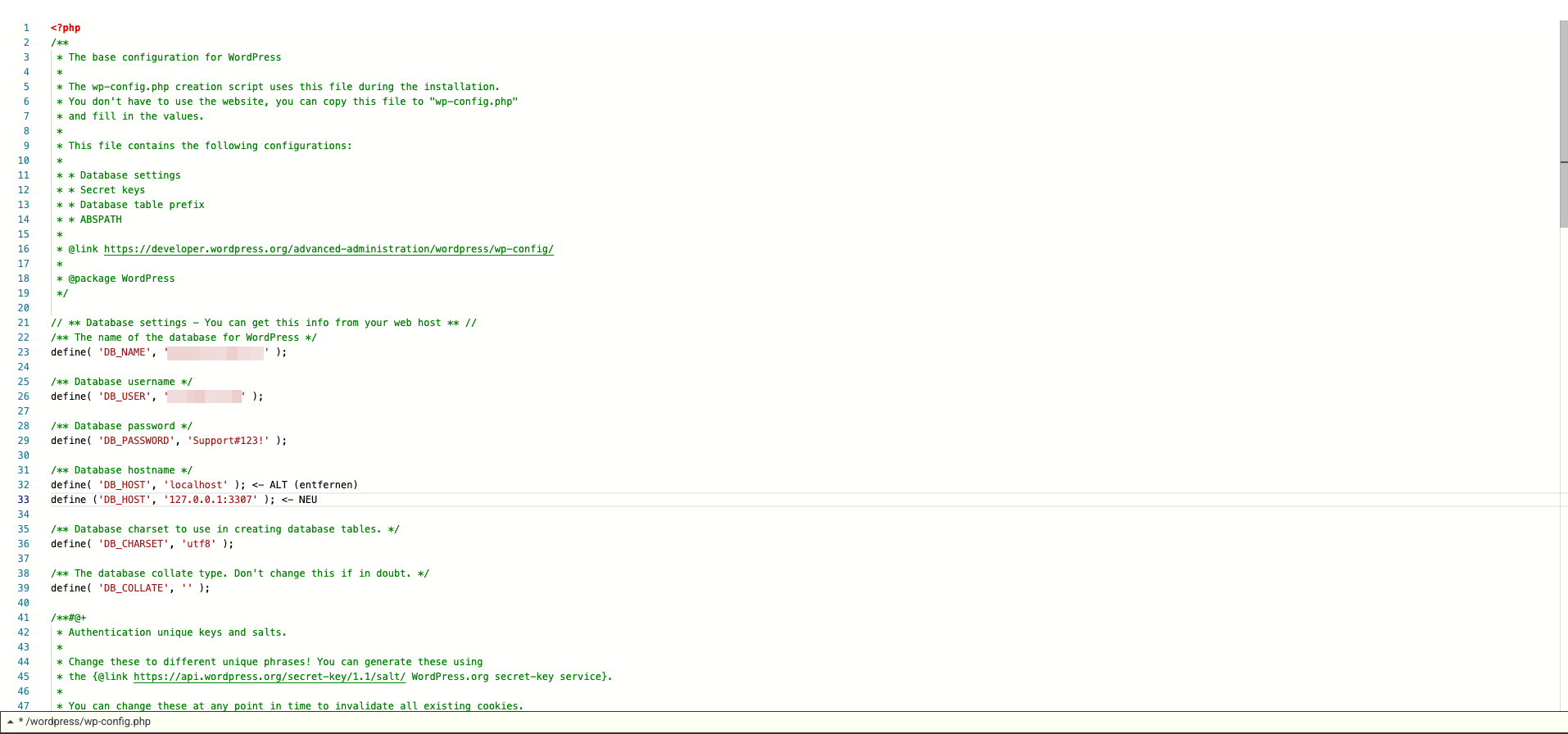
Keep the old values for safety in case problems occur.
7. Test whether the website works correctly with the new MySQL 8 database. This depends on the themes and plugins used. If problems occur, you can always revert the changes in the "wp-config.php" file to return to the old database.
Detailed instructions for WordPress in the Control Panel
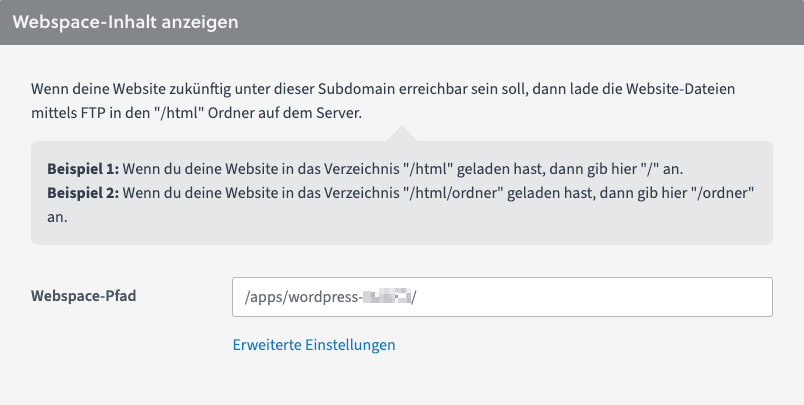
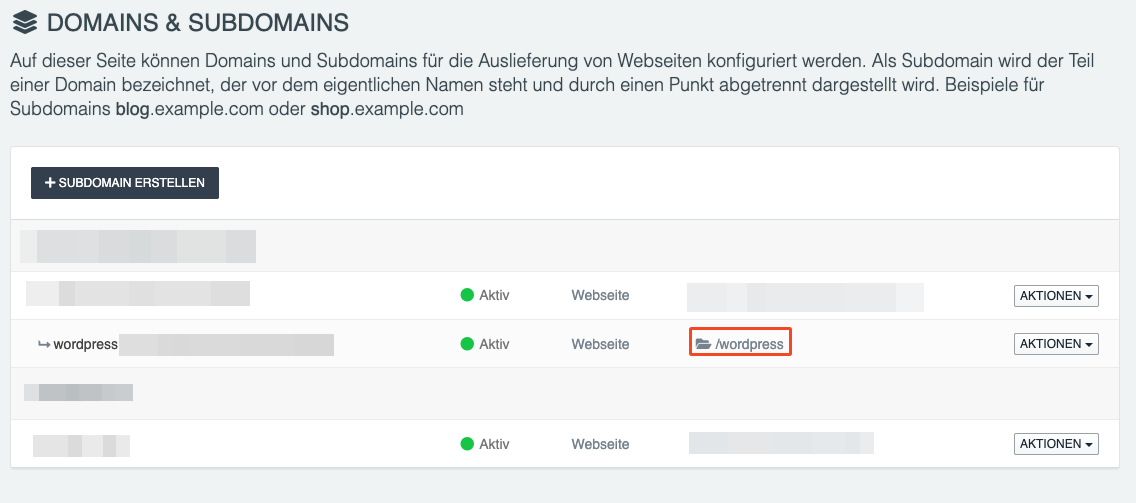
1. Open your WordPress installation via [Domain] – the affected domain – [Subdomain]. There you will find the entry "Webspace content" which shows the location of the WordPress installation.
2. In the specified folder, you will find a file called "wp-config.php" which contains the database information including the password. To access it, go to [Webhosting] – [Web-FTP], right-click on the file "wp-config.php".
3. Use the data found in step 2 to log in to the corresponding database via [Webhosting] – [Databases] – [Call phpMyAdmin for this database]. Then export the database.
4. Create a new database with MySQL 8 and the same password. Also log in via [Call phpMyAdmin for this database].
Before you can import the database, you need to edit it. Open the exported database file in a text editor of your choice. Look for the following lines, which are usually between lines 21 and 24:
-- Database: `XXXX`
--
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `XXXX` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci;
USE `XXXX`;
Replace "XXXX" with the name of the new database and save the changes.
5. Import the previously exported database into the newly created MySQL 8 database.
6. Now you need to adjust the host and database name. In the case of WordPress, you can do this in the "wp-config.php" file. Depending on whether you manage your web hosting in our Control Panel or in Cloudpit, the database server differs.
For customers in the Control Panel, the correct address is mysql80.local:3307.
Keep the old values for safety in case problems occur.
7. Test whether the website works correctly with the new MySQL 8 database. This depends on the themes and plugins used. If problems occur, you can always revert the changes in the "wp-config.php" file to return to the old database.